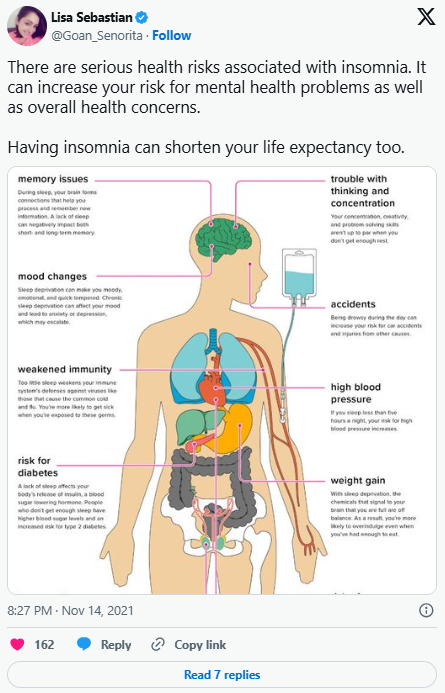
Insomnia in Older Adults is a condition that affects many elderly people, significantly impacting their physical and mental well-being. As individuals age, their sleep patterns often change, and insomnia can become a common issue. The importance of getting a good night’s rest is well-known for maintaining overall health, but for older adults, this becomes even more crucial. Sleep is vital for cognitive function, emotional balance, and physical health, so when insomnia sets in, it can have severe consequences.
How Insomnia in Older Adults Affects Cognitive Health
Many older adults struggle with staying asleep or experiencing interrupted sleep cycles. This lack of sleep can lead to more than just fatigue—it can cause cognitive decline. Insomnia in older adults has been linked to an increased risk of dementia and other cognitive impairments, which can creep up slowly over time and may not be immediately noticeable.
The Health Risks of Insomnia in Older Adults and Medication
The use of sleep medications is common among those trying to manage their insomnia. While they can provide temporary relief, these medications come with their own set of risks, particularly for older adults. Research suggests that frequent use of sleep aids in older individuals could actually increase the likelihood of developing disabilities. The physical side effects of these medications can affect balance, coordination, and even contribute to an overall decline in health.
In conclusion, insomnia in older adults not only disrupts sleep but also places them at a higher risk for a range of health complications. It’s important for older adults to explore alternatives to medication, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, and seek professional guidance to ensure that their sleep is both restorative and healthy.
Source: www.inquisitr.com



